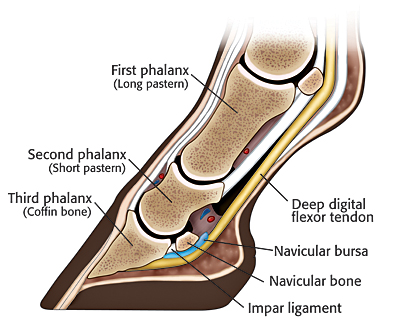
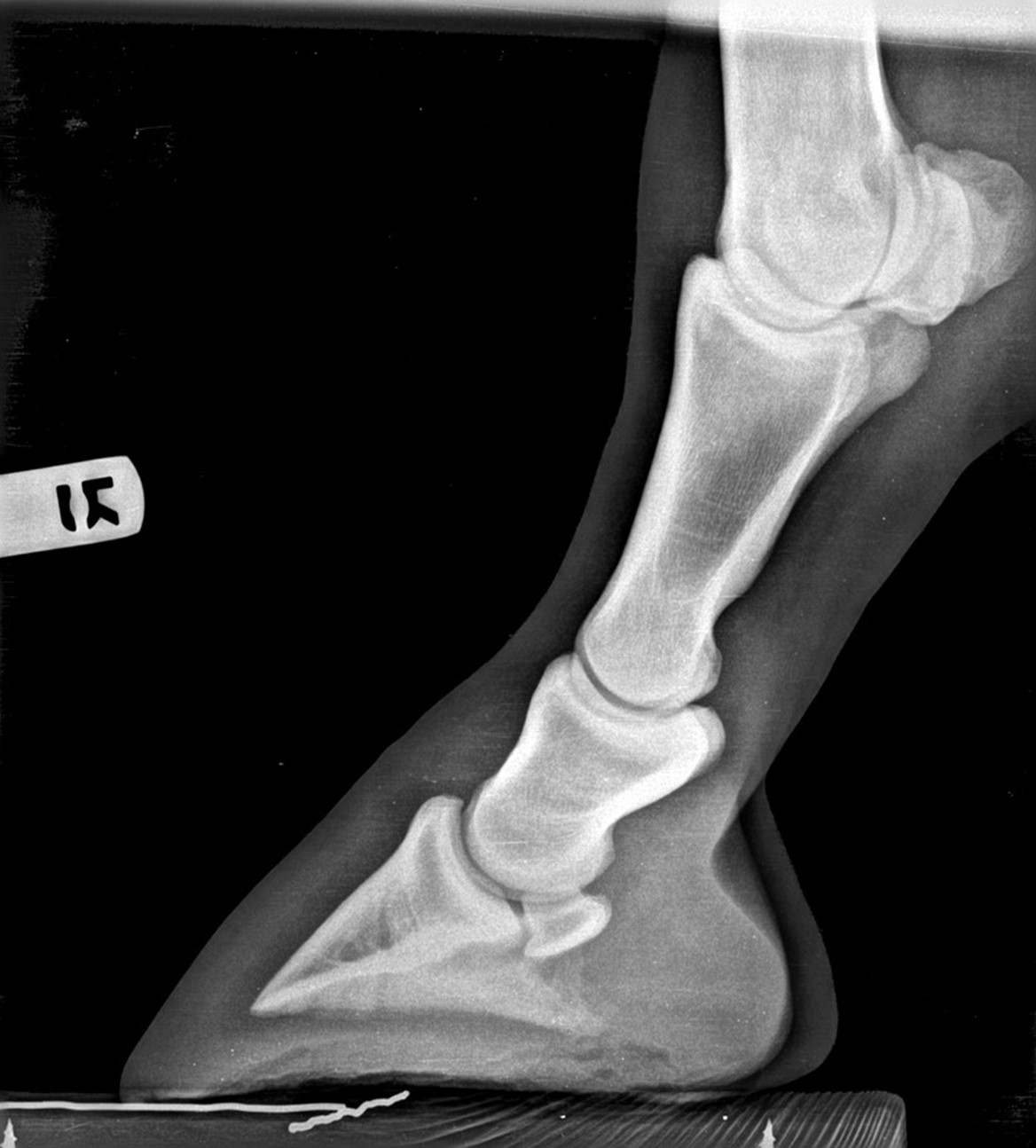
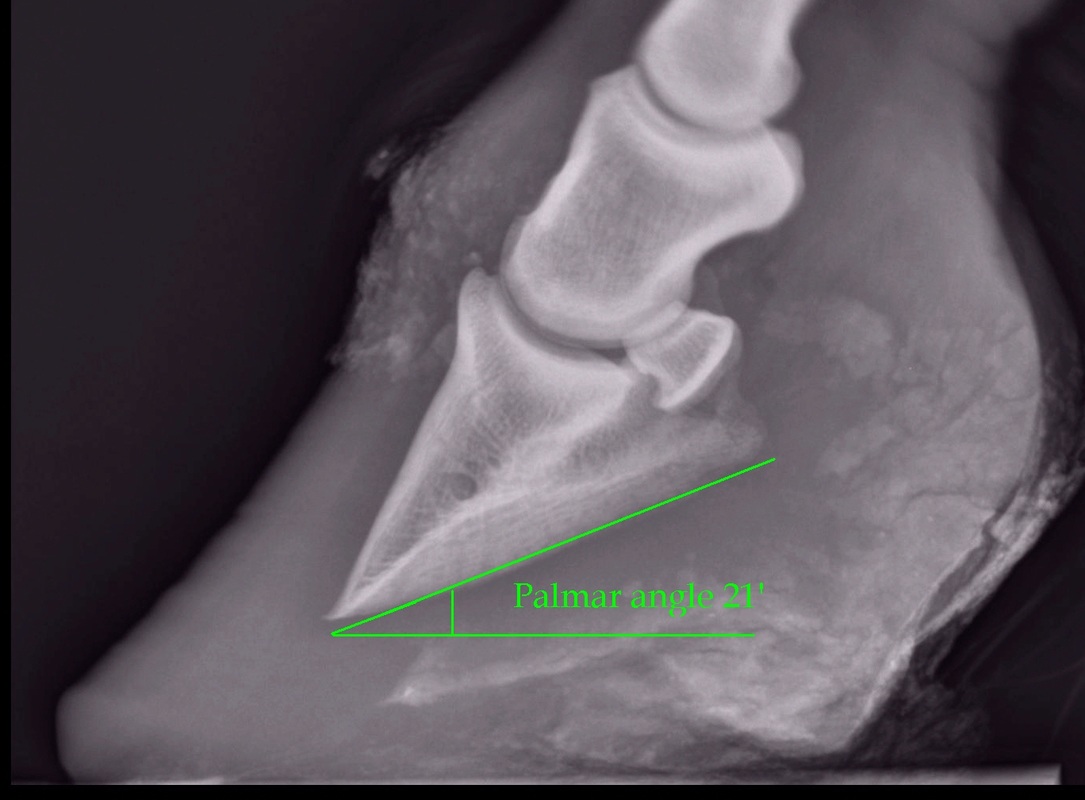
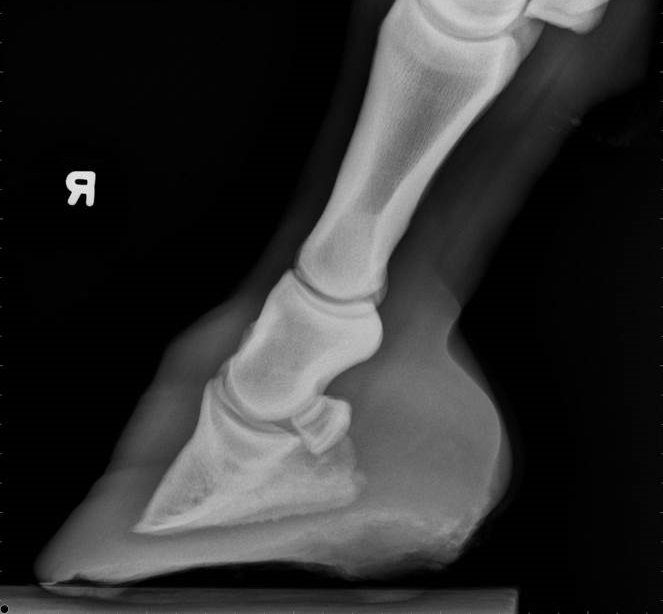
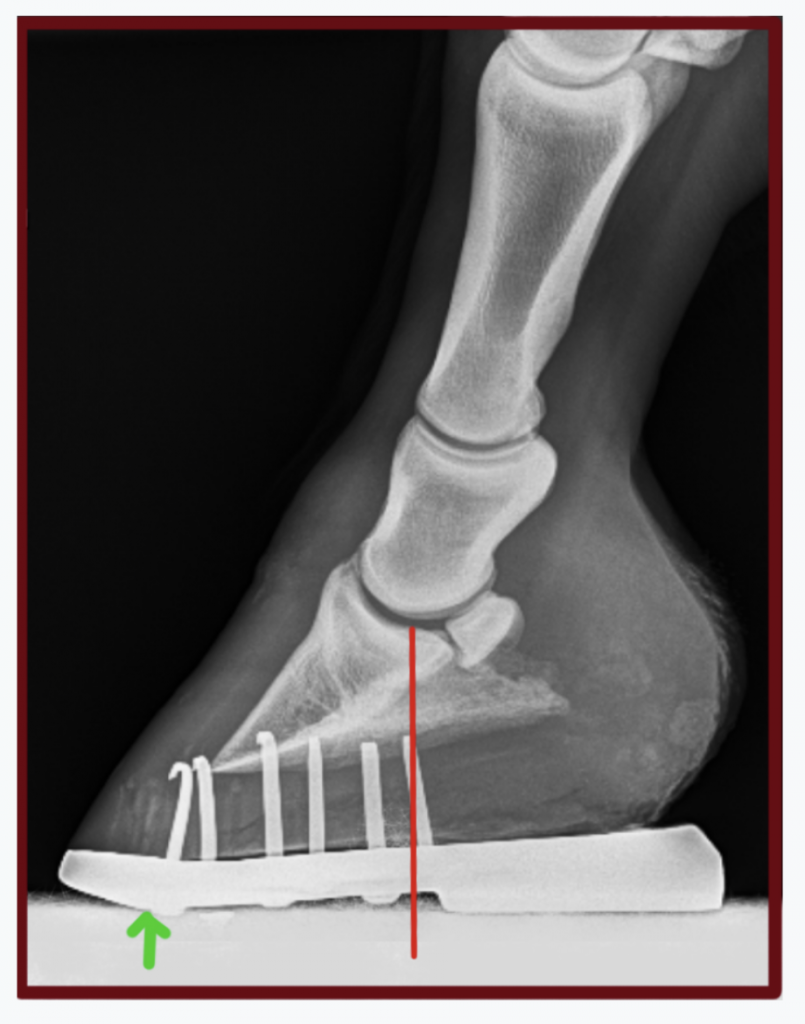
The xray will show whether the hoof pastern axis is parallel If the axis is broken forward (club foot) or if the axis is broken back (long toe underrun heel), the radiograph will reveal the degree of deformity and the best way to trim the foot to improve it Using landmarks, measurements can be drawn on the radiographs and transferred to the foot• rotatory subluxation of talocalnoenavicular joint (subtalar) complex with talus in plantar flexion and subtalar complex in medial rotation and inversion • also reffered as clubfoot • talipes derived from term talus ankle & pes foot • equinovarus derived from word equino like a horse & varus turned inward 4A club foot is a DEFORMITY and for any horse to win at top level competition it needs every possible advantage and no drawbacks The only way to stop continuing problems with club footed horses is not to breed from them After 11 months of gestation, it is a costly and heart breaking exercise if it results in a club footed foal

Severe Lameness Scarsdale Vets
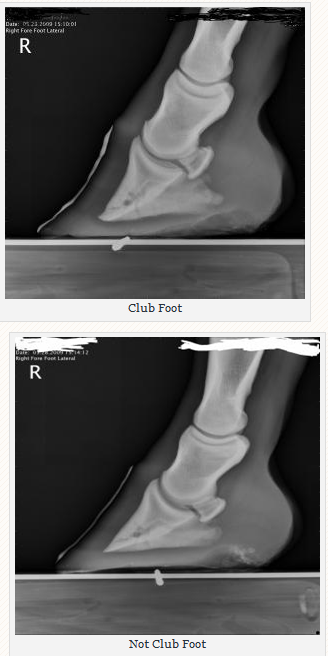
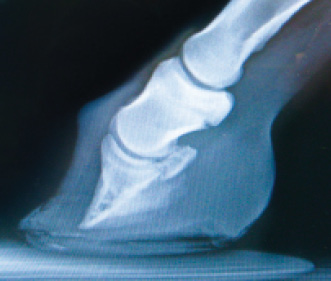
Club foot horse x ray
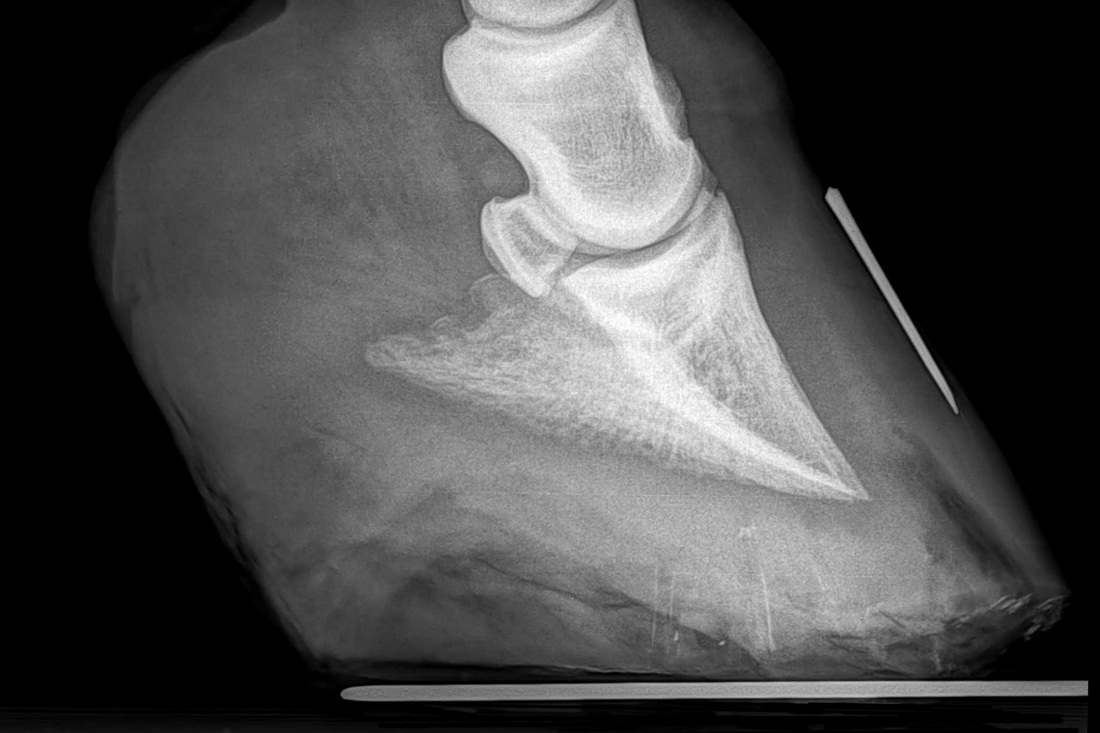
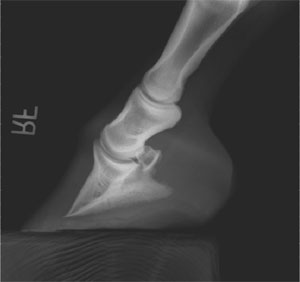
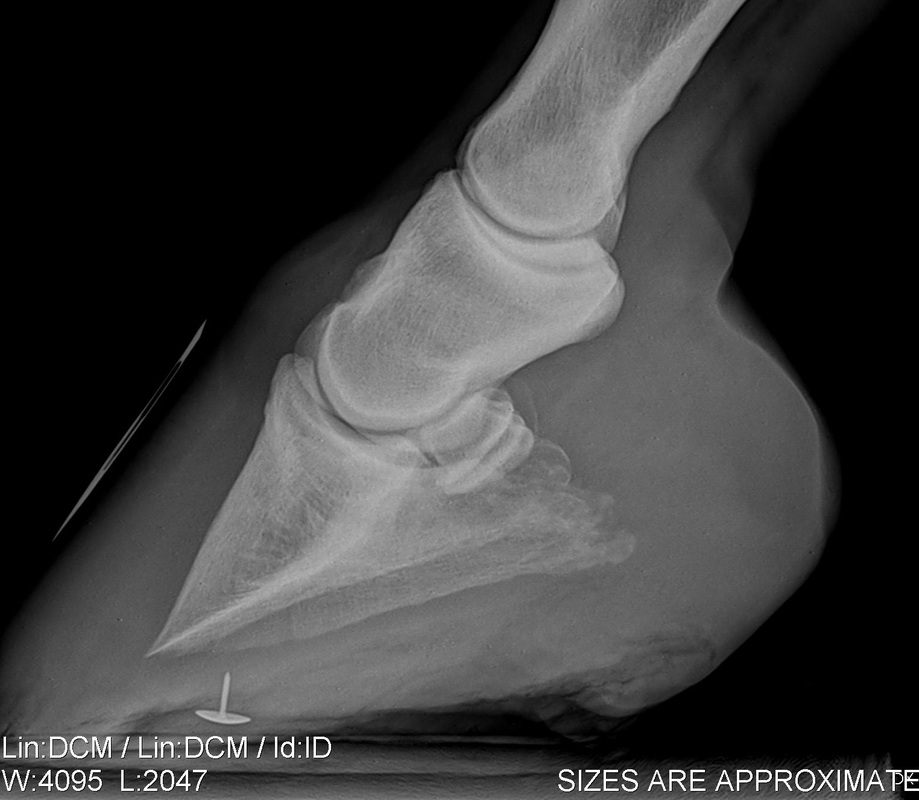
Club foot horse x ray-An X ray of your horse's foot can help you predict the future while it shows you the present MECHANICAL LAMINITIS TREATMENT Foot X Rays A Crystal Ball? Apparently the club foot condition has been with this horse since it was a foal whereas a dish at or just above the end of the toe would likely be considered grade 1 or 2 This club foot, as seen in photo 2, Photo 9 is the lateral xray showing the remodeled bone and poor quality of the bone



Equine
♦ Broden's views These views are taken with 10, , 30, and 40 degrees cranial angulation of an Xray beam focused at the tip of the fibula, with ankle rotated 45 degrees internally Excellent view of posterior subtalar joint given by these views helps in intraoperative monitoring of calcaneus fracture reduction and assessment of postoperative fusion status of Understanding hoof Xrays Horse & Hound 31 July, 06 1237 Diagnostic techniques For many years, Xrays have been the major imaging technique for evaluation of the foot, for both diagnosis andCheck out our x ray horse selection for the very best in unique or custom, handmade pieces from our shops
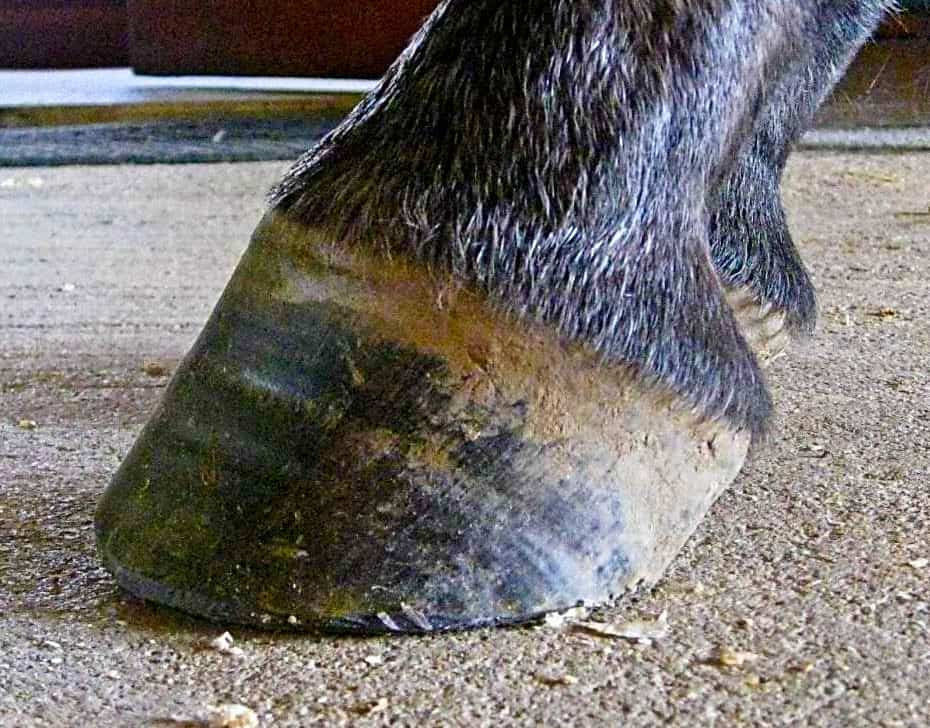
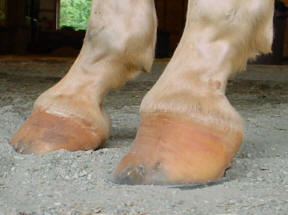
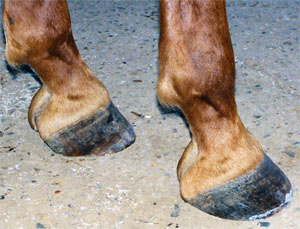
Symptoms of Club Foot in Horses Lameness Pain Excess toe wear Shortening of the tendon that is attached to the coffin bone Impacts the standing or movement of your young horse It can affect one or both limbs usually in the fore limbs Coronary band may bulge as the deformity progressesTwo studies evalu ated the effect of horse stance on measurements of the hoof capsule or phalanges 45 In the first, lateromedial radiographs of the front feet of five horses were acquired with the metacarpal region positioned vertically, and at various degree s angled cranially and caudally, as well as with the forelimbs only positioned on raised blocks 4 The angle of the solear A club foot alters a horse's hoof biomechanics, frequently leading to secondary lamenesses Affected horses tend to land toefirst, and their heel's growth rate is
Radiographs – xrays are taken by the veterinary surgeon to assist in diagnosing conditions relating to both the skeleton and soft tissues of the horse Conventionally, xrays have been taken using ionising radiation which is captured on a film The varying densities of tissues in the patient absorb some of the radiation so the xrayShoeing options for the Club Foot in Horses Do you have any recommendations on glue on horse shoes My 15 year old Paint horse gelding was born with a club foot He wears Cavallo simple bootsThe equine club foot is defined as a hoof angle greater than 60 degrees What we see externally as the equine clubbed foot is actually caused by a flexural deformity of the distal interphalangeal joint (coffin joint) Causes include nutritional issues, heredity, position in the uterus or injury The condition is most often encountered in young animals and can be either congenital (they are born




How To Manage The Club Foot Birth To Maturity The Horse



So Called Club Foot By James R Rooney Dmv
The previous trainer mentioned the horse had a clubfoot but the vet who performed the Press J to jump to the feed Press question mark to learn the rest of the keyboard shortcutsBy Christy West, TheHorsecom Webmaster Article # 9805 When you look at a radiograph (X ray) of a horse's foot, do you visualize soft tissues, or do you only see bones? "If you have a broad rule or method that you apply to all horses, it may work on some but it won't work on others You need to be open to many methods, and creative, and try to understand what caused this club foot Having xrays can be helpful, to determine sole thickness and the shape of the coffin bone and whether there is any rotation




Laminitis Signalment Treatment And Prevention Flying Changes



The Chronicle Of The Horse
An X ray of your horse's foot can help you predict the future while it shows you the present MECHANICAL LAMINITIS TREATMENT Foot X Rays A Crystal Ball? Club foot is one of the most common deformities in the horse world Horses affected with club foot develop a flexural deformity of the coffin joint, due to a shortening of the musculotendinous unit that starts high up in the limb and inserts on the coffin bone in the foot, resulting in an upright conformation of the footThe search terms (horse* OR equine*) AND (foot OR feet OR digit* OR hoof OR hooves OR phalan * OR navicular) AND (radiograph* OR radiolog *) were generated and input into the PubMed search engine Following exclusion of studies more than 5 years old and those determined not to relate directly to the question, six useful results regarding radiology were yielded




Severe Lameness Scarsdale Vets



Thrush Cured Cowboy Pads And Copper Sulfate
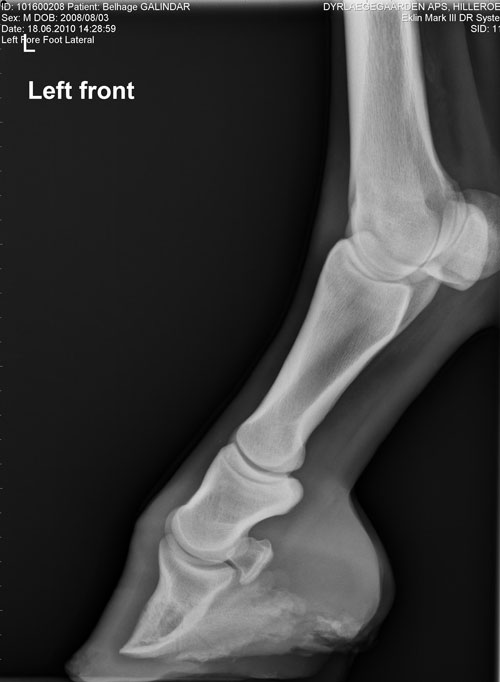
Radiographs, commonly known as xrays, are often taken during lameness exams to visualise the bones and joints Portable digital systems (DR) are mostly used for lower limb examinations and are especially useful if it is difficult or unsafe to travel an injured horse If your vet feels that xrays of the upper limbs, spine or thorax are needed In the horse, hoof growth is dictated in large part by weight distribution If a horse puts more weight on the inside of a hoof, the blood is pushed to the opposite side of the foot causing faster growth and wearing down the weighted surface at a faster rate With respect to the club foot, the heel of the affected foot grows faster and the hoofClub foot refers to a hoof that is more upright than normal It is often associated with a concave front (dorsal) hoof wall, high (often contracted) heels, and widening of the white line from mechanical stretching of the hoof wall attachments (the laminae) Adult club foot requires a completely different approach to treatment than juvenile club foot



Low Foot Case Study Dixie S Farrier Service



Podiatry The Equine Center
Lisfranc injury The 'Lisfranc' ligament stabilises the midforefoot junction Loss of alignment of the 2nd metatarsal base with the intermediate cuneiform indicates injury to this important ligament Every posttraumatic foot Xray must be checked for loss of alignment at the midfootforefoot junction (tarsometatarsal joints)Comes very useful in horses with upright feet, the best example being the clubfooted horse As the foot grows out in these horses, there is a propensity for the dorsal wall to distort and flare, producing multiple angles to the dorsal wall Radiographic evaluation of the dorsal wall with a conforming marker allows accurate assessment of the√画像をダウンロード horse club foot xray Club foot horse x ray Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals Club foot horse x ray Club foot horse x rayUnderstanding X Rays The Laminitis Site




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals




Farriery For The Hoof With A High Heel Or Club Foot Semantic Scholar
Xrays (correctly called radiographs) are essential for assessing changes in the feet following laminitis, and should clearly show the relationship between the hoof capsule and the internal structures of the foot to help the hoofcare professional Correctly marked and positioned xrays can be used to assess the severity of changes/damage, reach a prognosis, and monitor response T x 1 December 14 #2 B be positive WellKnown Member 1 December 14 #2 Joined 9 July 11 Messages 19,399 catembi said for a horse really reluctant to move forward I would be more inclined towards its feet giving very low grade pain, a minor inbalance can be enough to make them feel they cannot move but if bilateral will not show Club Feet Prevention, Treatment & Correction Anyone who has spent any time with equines has undoubtedly seen club feet A club foot horse is typically recognized and defined as having one front hoof growing at a much steeper angle than the other, with a short dished toe, very high heels, extremely curved wall and straight bars The club foot is also generally much




Equine Podiatry In Wendell Nc Neuse River Equine Hospital



Managing The Club Hoof Easycare Hoof Boot News
I took my horse to the vets for nerve blocks and xrays last year and the total cost was unbelievable!!!!, the X Rays alone were £133 to basically plug the machine in then £15 per x ray Just make sure your vet doesn't get 'snap happy' as mine didI was not happy when I got the bill To come out and X Ray for £0 sounds a bargain The contracted muscle/club foot condition is a common growth problem in young horses (up to 6 months of age), causing upright pasterns and a tiptoe stance This is often seen in foals with developmental problems due to rapid growth If discovered soon enough, this condition can be reversed by altering the foal's diet and reducing stress onXray examination Xray examination can help determine the relative positions of the pedal bone and hoof wall and assess shoe placement (Figure 6) FiGURe 6 the FRont oF the hooF w All And pedAl Bone shoUld Be pARAllel the pedAl Bone shoUld Be 510 deGRees FRoM the GRoUnd BeARinG sURFAce the centRe oF A ciRcle ARoUnd the coFFin



Contact Us Palmetto Equine Veterinary Services




Hoof Evaluation Radiographs For The Farrier
Written and presented April 12 by RF (Ric) Redden, DVM To better understand the club foot syndrome, we must be familiar with the mechanical formula and how it greatly influences the various degrees of hoof capsule distortion and bone remodeling associated with this syndrome There appears to be a direct relationship between the degree of tension increase or contributiveClassification system designates four grades of clubfoot2,8 A grade 1 clubfoot has a hoof axis 3° to 5° greater than the contralateral foot and displays fullness at the coronary band but is mild enough that the hoofpastern axis is aligned A grade 2 clubfootClub foot horse x ray Clubfoot is a birth defect where one or both feet are rotated inward and downward The affected foot and leg may be smaller in size compared to the other Approximately 50% of cases of clubfoot affect both feet Most of the time, it is not associated with other problems Without treatment, the foot remains deformed, and people walk on the sides of their feet




How To Treat Club Feet And Closely Related Deep Flexor Contraction



Equine Podiatry Say What Mobile Veterinary Services
Post by sophielouise on at 304am When Chester had both front feet xrayed at 'home' (numerous 'takes', if you like) I think the xrays were about £150 It must have been a mobile unit I think, as they came out to the yard and set up in a spare box and the Xrays were instant on a laptopIn the club foot because the deep flexor tendon is contracted, the xray will show that the pedal bone angles are quite different, the front is not in line with the hoof wall, the tip is pointing down and the rear part is much greater than five degrees Put simply, the heels will need to be lowered and any flare corrected at the toeAlmost always, I am called to club foot cases when the horse goes lame on the normal side This is usually caused by people trying to force the hooves to match each other This thinking often leads a farrier to cut the sole out from under P3 at the toe and allow the heels to grow unchecked on the normal foot Two wrongs don't make a right Treat the hooves as individuals, figure out the trueClub Foot Horse X Ray




The Truth About Hoof Pastern Axis




Hoof Evaluation Radiographs For The Farrier
A horse can still be a good riding horse for a long period of time, despite having xray pictures with findings" Says Prof Dr Lischer, member of the xray commission and director of the equine clinic of Freie University of Berlin However you can still make an agreement between buyer and seller in determining how many xrays to make Club Foot Heritability in Horses The normal alignment of the short pastern bone and coffin bone is a straight line visible on X ray, but inPositioning the foot for the examination Blocks are needed to elevate the off the ground allowing the foot to be centered in the cassette and the xray beam to pass horizontally through the specific area of interest (ie solar surface of the foot, DIP joint, navicular, etc) The foot should be placed as close the inside of the block when taking a lateral image (to place the cassette as




No Foot No Horse Part 2 Hayes Equine Veterinary Services



Hoof Radiographs Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic
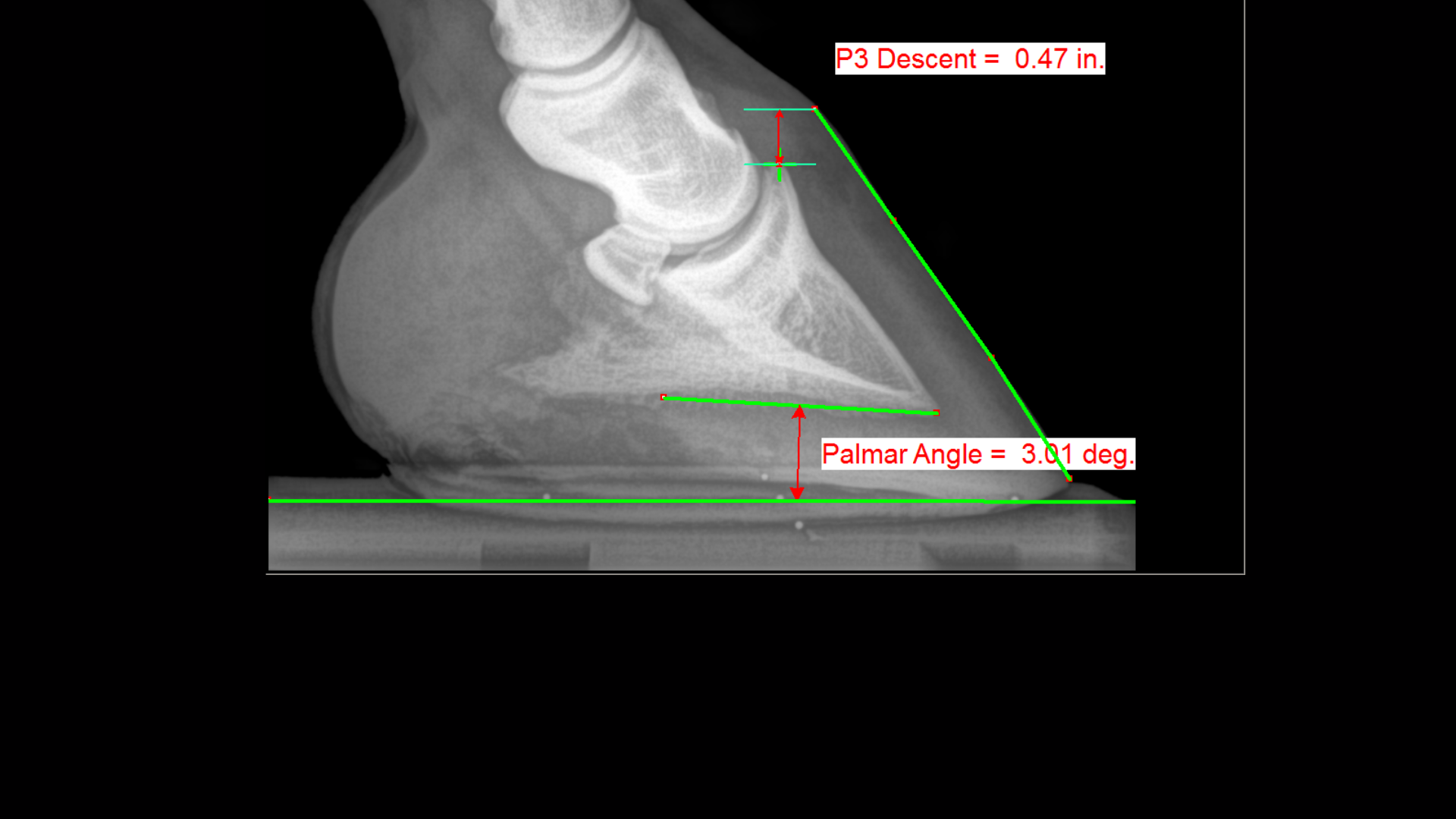
Xray of feet (typical clubfoot) Clubfoot Introduction Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus – TEV) is one of the major orthopedic conditions of childhood One of the most common of all birth defects, clubfoot affects about 1 in 400 babies born in the United States each year Boys are affected twice as often as girls The xrays showed fractures in the lateral cartilage (or sidebones) on both front feet The vet said these fractures were due to the extreme pressure put on the cartilage (due to the size and placementof the sidebone) and also the lack of shock absorption (due to heel contraction and size of the hoof) The same horse's radiographs give the same information Fig 7 and 9 were taken a year before I first saw the horse and the photo above was taken It appears the sole was a bit thicker, rotation less and distal descent less severe at that time, than what I



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia




Radiographic And Radiological Assessment Of Laminitis Sherlock 13 Equine Veterinary Education Wiley Online Library
A horse with club foot has one hoof that grows more upright than the other The "up" foot is accompanied by a broken forward pastern, that is, the hoof is steeper than the pastern (Photo 1) In a normal foot, the hoof capsule and the pastern align Radiographs will show that the boneyClub Foot Horse X Ray It is often associated with a concave front (dorsal) hoof wall, high (often contracted) heels, and in many cases, mild club foot is not associated with lameness or decreased performance Abenteuer pferde von schleich horse club Horses feet are placed on x ray transparent 'lifts' or blocks to enable x rays to showFor this reason, particularly with older horses, it is strongly advised to start with an Xray of the foot in question If the joints are unaffected, then there is little reason not to proceed – indeed, when hoof capsule rotation is so severe that the point of the P3 is the principle point of support for the horse, then action is an absolute necessity



Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site




Laminitis A Pictorial Review
We've gathered our favorite ideas for Equine Carpus X Ray, Explore our list of popular images of Equine Carpus X Ray Photos Collection with high resolution




The Importance Of Physical Maturity In The Horse Horsetalk Co Nz



Barehoofcare Com




Filly With Club Foot Barefoot Hoofcare




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses



Performanceequinevs Com



Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles



Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site



Sports Medicine And Lameness Palmetto Equine Veterinary Services



Types Of Crooked Legs In Foals



ep Org




Foal With Hoof Problems Club Foot The Horse



Comstock Equine Hospital Veterinarian In City State Country Corrective Trimming




Radiolucency Glue On Horseshoes By Sound Horse Technologies




Clubfoot Barefoot Hoofcare




Hoof Evaluation Radiographs For The Farrier




Club Foot In Horses Brian S Burks Fox Run Equine Center Facebook




Michael Porter Equine Veterinarian 12



Avmajournals Avma Org



The Tolerable Club Foot The Horse




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource



Equine




Natural Angle Volume 15 Issue 1 Spanish Lake Blacksmith



Club Foot



Understanding Navicular Syndrome Heel Pain In Horses



Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site




Michael Porter Equine Veterinarian 12



ep Org



Frequent Trips Aid Club Foot American Farriers Journal



ep Org



ep Org



Club And Subluxation In The Proximal Interfalangian Articulation Farriers Forum



1



1




Fighting Laminitis Expert How To For English Riders



Theneaep Com




Clubfoot Barefoot Hoofcare



Theneaep Com
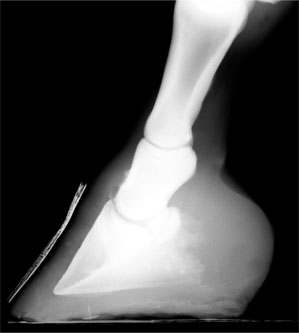



Frequent Trips Aid Club Foot American Farriers Journal




Pin On Club Foot




Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome



Hoof Care For The Club Footed Horse David Farmilo
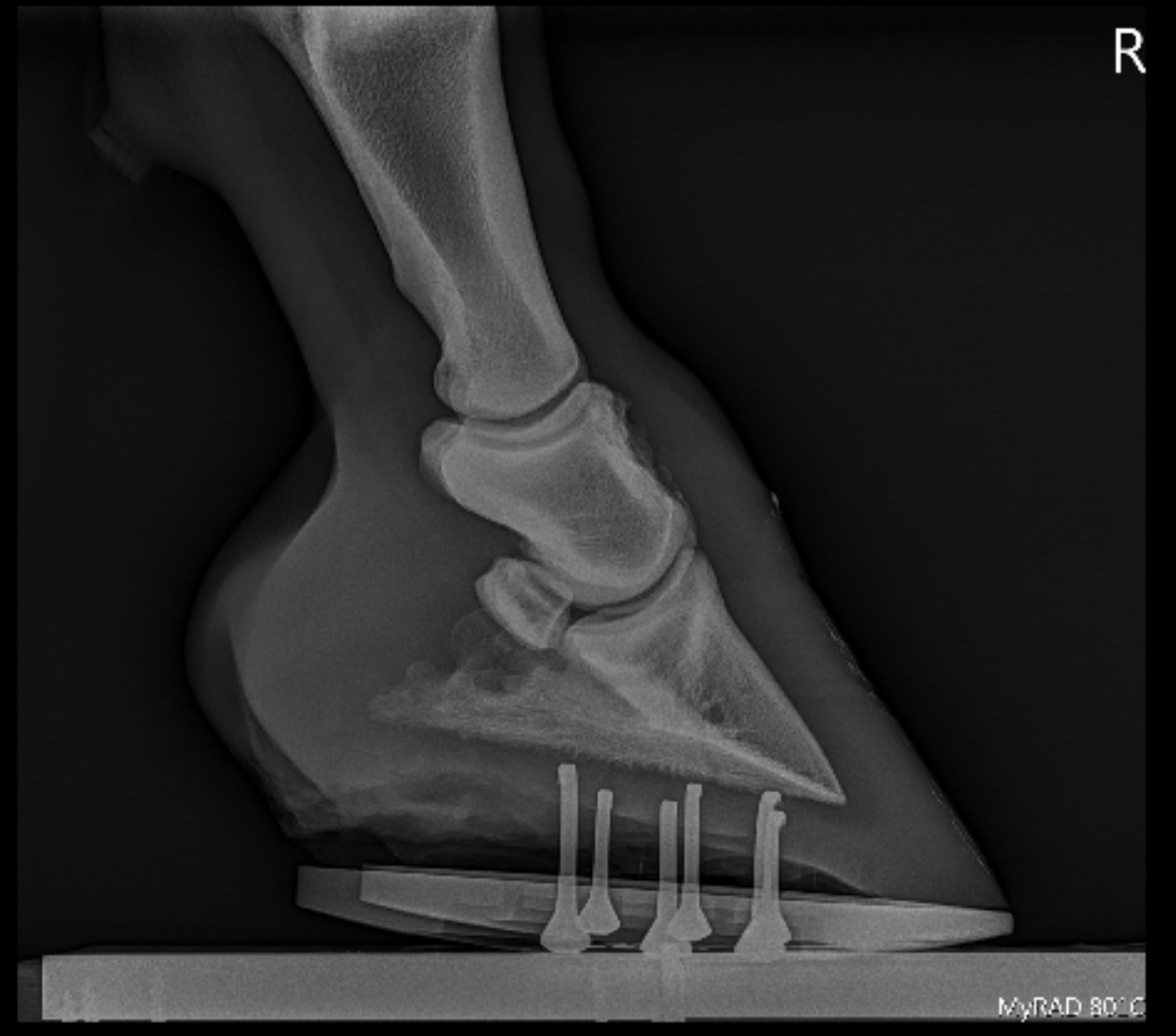



Podiatry Burwash Equine Services




Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome



Theneaep Com




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses




Radiographic Exposure Settings Hints And Tips Equine Imv Imaging




Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles American Farriers Journal




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals




Does My Horse Have Pyramidal Hoof Disease The Horse



Equine Podiatry Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles



Barehoofcare Com




Fighting Laminitis Expert How To For English Riders
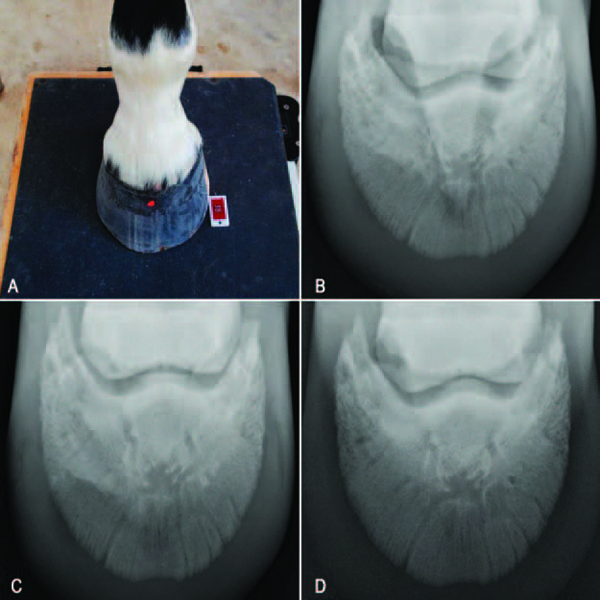



Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles




Being Able To Read X Rays Of The Equine Documentalist Facebook




Puncture Wounds In The Foot Vetsouth



Boarding At Yucca Veterinary Medical Center




Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site




The Wild Mustang Hoof
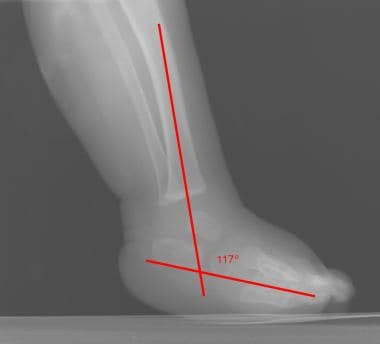



Clubfoot Imaging Practice Essentials Radiography Computed Tomography




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals
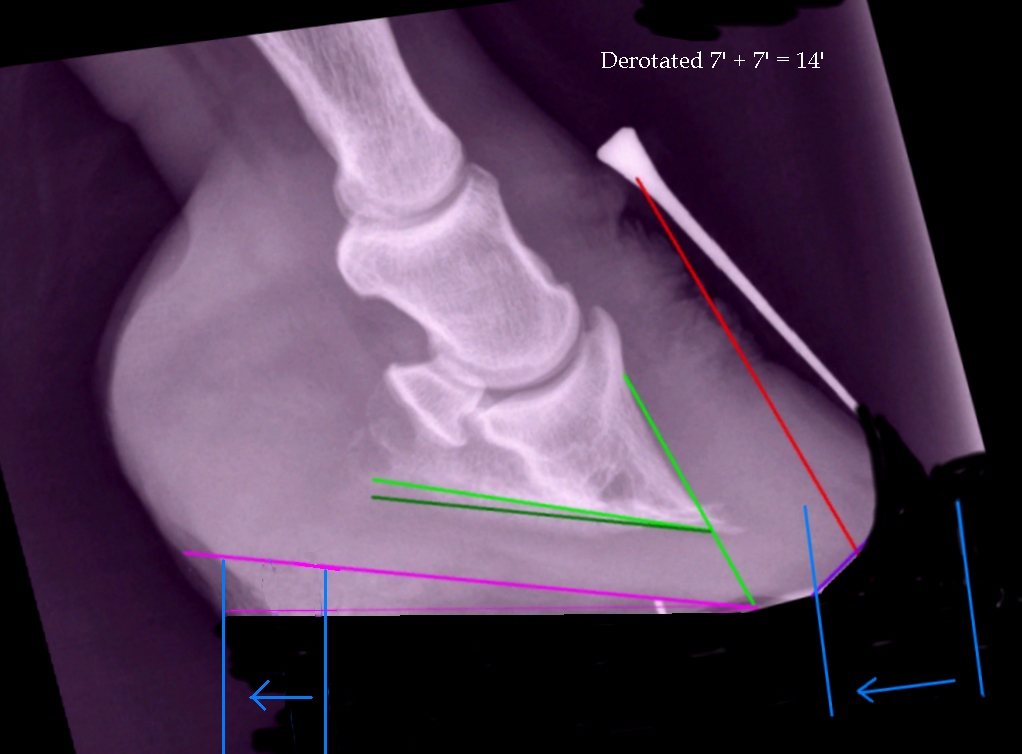



High Heels The Laminitis Site



1
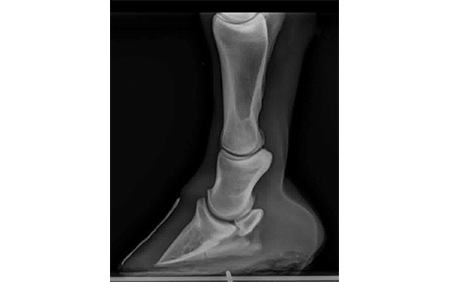



Equine Laminitis Soft Ride Boots For Equine Laminitis Comfort




Innovative Equine Podiatry Navicular Case Examples



Low Foot Case Study Dixie S Farrier Service



Horseandriderbooks Com




The Wild Mustang Hoof




The Progressive Equine Services Hoof Care Centre Facebook
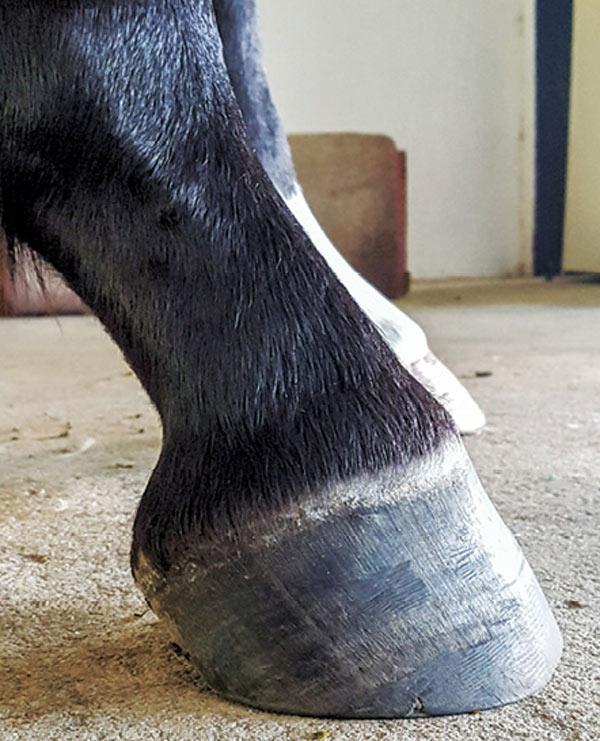



Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles American Farriers Journal
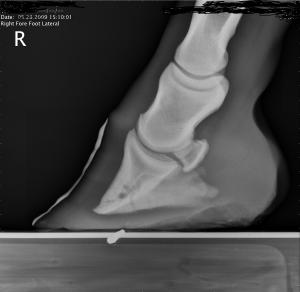



Club Foot Or Not Barefoot Hoofcare




Radiography Of The Equine Stifle Part 4 Of 4 Imv Imaging




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Epublishing



Viewing A Thread Ringbone Help




Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome



Basic Shoeing Working With A Club Foot Farrier Product Distribution Blog




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource



Farrier Terms Decoded Top 5 Farriery Terms Horse Owners Should Know Badger Veterinary Hospital




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Hoof Deformities Round Pen Square Horse



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿